Main Point
The study explores the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare practice based on an extensive scoping review. While AI holds promise to transform healthcare, the empirical evidence reveals a dissonance between research promises and the slow adoption of AI systems in practice. The majority of implemented AI systems in healthcare have low action autonomy, serving as decision support tools with minimal disruption to workflows. However, research on the implementation process is still in its early stages, and there is a lack of consensus on the definition of implementation.
5 Salient Points
Dissonance between Research and Practice: Despite the large promises of AI in revolutionizing healthcare, the slow adoption of AI systems in routine practice remains a challenge.
Predominance of Low Action Autonomy AI Systems: Most AI systems implemented in healthcare are decision support tools with low action autonomy, rather than more disruptive AI systems.
Need for Research on Disruptive AI Systems: There is a need for more empirical research on the implementation processes of disruptive AI systems, which have higher action autonomy and greater potential to impact healthcare delivery significantly.
Lack of Clear Motivation: Many studies do not provide a clear motivation for implementing AI systems, indicating a gap between research-driven goals and clinical practice needs.
Call for AI-Specific Implementation Framework: To facilitate successful adoption of AI in healthcare, there is a demand for the development and dissemination of AI-specific implementation frameworks that address unique aspects of AI adoption, such as building trust, transparency, and ethical considerations.
📝Research Appendix
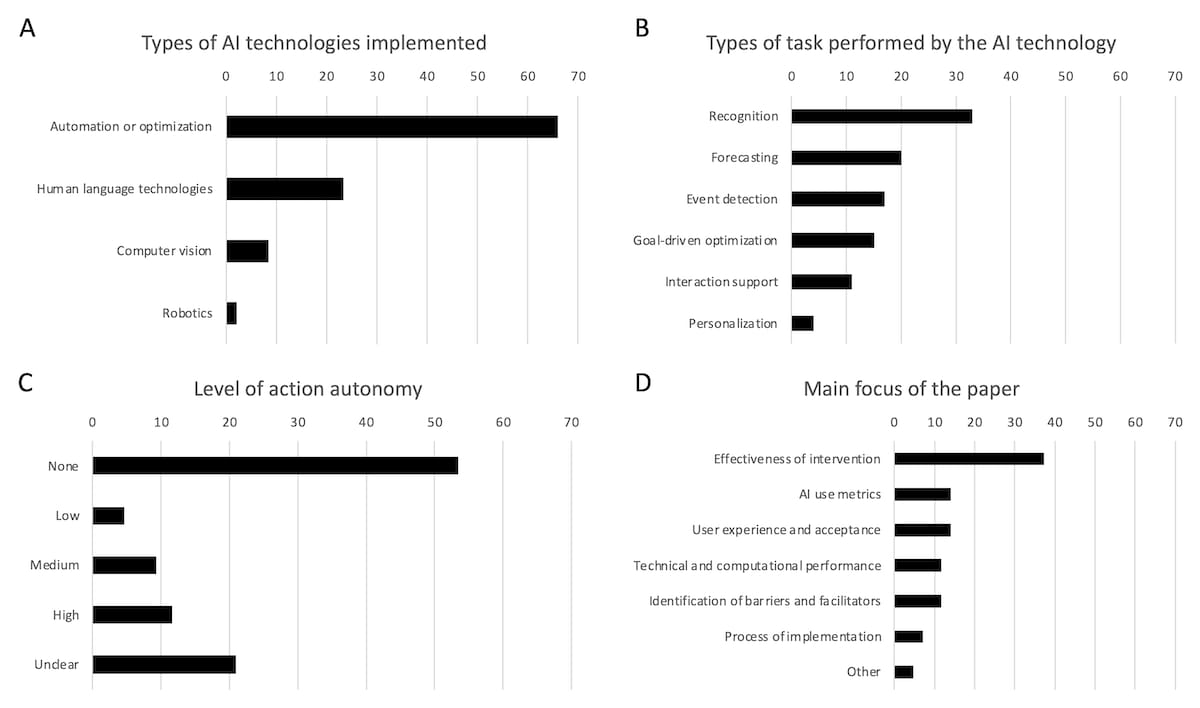
Types of artificial intelligence (AI) systems implemented and main focus of research.

Eligibility criteria and their rationale.

